
ph: +96560443060
alt: +919689983542
jacksanf
- Home
- About Us
- Services
- Contact Us
- Prayer Request
- Testimonials
- Dr Jacksan Therapy

- Life Lessons

- 30 Things to Start Doing for Yourself
- 9 Ways to Become an Optimist
- 10 Mistakes Unhappy People Make
- 60 Selfless Ways to Pay It Forward
- 101 Important Life Principles To Live By Every Day
- 60 Tiny Love Stories to Make You Smile
- 15 Reasons to Run for Your Life
- 10 Life Lessons People Learn Too Late
- 25 Things I Would Tell My 20-Year-Old Self
- 10 Critical Questions You Must Ask Yourself
- 12 Unconventional Habits of Highly Productive People
- 9 Things to Think About Before You Give Up
- 15 Ways to Live, and Not Merely Exist
- 12 Things You Should Be Able to Say About Yourself
- 20 Things to Start Doing in Your Relationships
- 50 Things Everyone Should Know How To Do
- 28 Dignified Ways to Impress Everyone Around You
- 12 Universal Skills You Need to Succeed at Anything
- 7 Things Happy, Healthy People Do Every Morning
- 10 Habits of Happy, Healthy Couples
- 10 Powerful Steps to Stop You from Judging People
- Yoga Cds for sale
- Learn Yoga in Goa
- Yoga practice and uses by Jacksan
- Skype yoga sessions
- Hatha Yoga for Life Book
- Yoga Practice Videos by Dr Jacksan
- Intake Form
- Psychological Counseling Intake Form
- Feedback Form
- Yoga Feedback Form
- Kickboxing
- Ecstasy Album Video
- Learn Salsa Video
- Basic and Advanced Salsa Videos
- Zumba
- Do I need Therapy Test
- Free Ebooks
- Products for PowerPoint Presentations
- Career Test

- Questionnaire on self-esteem
- Student Motivation Survey Self-Assessment
- Career Profile Analysis
- Domestic Violence Screening Test
- Woman Abuse Screening Tool
- Battered Woman Test
- Dissociative Experiences Scale
- Parent-Child Internet Addiction Test
- Free Fitness Profile
- Alcoholism Test
- Drug Abuse Screening Test
- Sexual Addiction Screening Test
- Gambling Test
- ADHD Quick Screening Test
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder
- Panic Attack Test
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Test
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder Test
- Mood Disorder Questionnaire
- Stress: Workaholic Test
- Autism Spectrum Test
- Project on Emotional Intelligence

- Strength of Character
- Success factor
- Attitude
- Social Intelligence
- Content or restless
- Content or Restless 2
- Extrovert or introvert
- How assertive are you?
- Laterality
- Optimist or pessimist
- Aggression
- Adventurous or Timorous
- Adventurous or Timorous 2
- How patient are you?
- Planned or spontaneous
- Self-confidence
- Emotional
- How well do you cope under pressure?
- Tactful or undiplomatic
- Leadership factor
- Tough or tender
- Open or Close
- Open or Close 2
- Do you have the gift of thrift?
- How obsessive are you?
- Home Remedies and Natural Cures

- Abrasions
- Acne
- Acne Scars
- Alcoholism
- Allergies
- Alzheimer
- Amnesia
- Anemia
- Angina
- Anorexia
- Anxiety
- Appendicitis
- Arteriosclerosis
- Arthritis
- Asthma
- Athletes Foot
- Autoimmune Disease
- Back Pain
- Backache
- Bacterial Vaginitis
- Bed Sores
- Bedwetting
- Belching
- Blemishes
- Bloating
- Blocked Milk Duct
- Body Odor
- Body Rash
- Boils
- Bone Spur
- Breast Care
- Bronchitis
- Bruises
- Burning Tongue
- Burns
- Bursitis
- Cankar Sores
- Carpal Tunnel
- Cataract
- Celiac Disease
- Chafing
- Chest Congestion
- Chicken Pox
- Chlamydia
- Cholera
- Cirrhosis of the Liver
- Cold Sores
- Colitis
- Common Cold
- Common Digestive Disorders
- Dizziness
- Dry Skin
- Ear Infection
- Earache
- Eating Disorders
- Eczema
- Edema
- Endometriosis
- Enema
- ENT Disorder
- Eye Infection
- Female Sterility
- Fever
- Flatulence
- Freckles
- Frequent Urination
- Fungal Infections
- Gall Bladder Disorders
- Gastritis
- Genital warts
- GERD
- Gingivitis
- Goitre
- Gout
- Gray Hair
- Halitosis
- Hangover
- Hay Fever
- Head Congestion
- Head Lice
- Headaches
- Heat Stroke
- Hemorrhoids
- Herpes
- Hiccups
- High Blood Cholesterol
- High Blood Pressure
- Hives
- Hyperacidity and Heartburn
- Hyperthyroidism
- Hysteria Disorder
- Indigestion
- Influenza
- Insomnia
- Interstitial cystitis
- Intestinal Worms
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
- Itching
- Jaundice
- Jock Itch
- Kidney Stones
- Knee Pain
- Laryngitis
- Leg Cramps
- Lethargy
- Leucoderma
- Leucorrhoea
- Lice Treatment
- Liver Disease
- Loss of Hair
- Low blood pressure
- Low Blood Sugar
- Low Immunity
- Lyme Disease
- Malaria
- Mastitis
- Measles
- Menopausal Disorders
- Menstrual Cramps
- Menstrual Problems
- Migraine
- Moles
- Mononucleosis
- Morning sickness
- Mumps
- Nasal Congestion
- Nausea
- Nephritis
- Neuritis
- Nosebleeds
- Obesity
- Oral Candidiasis
- Orchitis
- Osteoporosis
- Palpitation
- Peeling Skin
- Peptic Ulcer
- Phlegm
- Piles
- Pimples
- Plantar Fascia or Plantar Fasciitis
- Pneumonia
- Poison Ivy
- Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
- Premature Ejaculation
- Premature Greying of Hair
- Premenstrual syndrome (PMS)
- Prostate Disorders
- Psoriasis
- Pyorrhoea
- Razor Burns
- Respiratory Diseases
- Retain teeth and lip color
- Rheumatism
- Ringworm
- Scabies
- Schizophrenia
- Scurvy
- Sexual Disorders
- Sexual Impotence
- Shoulder Pain
- Sinusitis
- Skin Blemishes
- Skin Disease
- Sleep Apnea
- Sleeping Disorders
- Snoring
- Sore Nipples
- Sore Throat
- Spring Ailments
- Stress
- Stretch Marks
- Sunburn
- Sweating Disorder
- Swimmers Ear
- Tennis Elbow
- Thinning Hair
- Throat Obstruction
- Thyroid
- Tinea Versicolor
- Tinnitus
- Toe Nail Fungus
- Tonsillitis
- Toothache
- Tuberculosis
- Underweight
- Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
- Urticaria
- Vaginal Infections
- Varicose Veins
- Vertigo
- Vomiting
- Warts
- Wheezing
- Whooping Cough
- Winter Ailments
- Womens Health Issues
- Wrinkles
- Yeast Infection
- Zits
- Raven Test

- TRIGUNAS TEST

Leadership factor

Good leaders are made not born. If you have the desire and willpower, you can become an effective leader. Good leaders develop through a never ending process of self-study, education, training, and experience.
To inspire your workers into higher levels of teamwork, there are certain things you must be, know, and, do. These do not come naturally, but are acquired through continual work and study. Good leaders are continually working and studying to improve their leadership skills; they are NOT resting on their laurels.
Definition of Leadership
Leadership is a process by which a person influences others to accomplish an objective and directs the organization in a way that makes it more cohesive and coherent. Leadership is a process whereby an individual influences a group of individuals to achieve a common goal.
Leaders carry out this process by applying their leadership knowledge and skills. This is called Process Leadership. However, we know that we have traits that can influence our actions.
This is called Trait Leadership, in that it was once common to believe that leaders were born rather than made. These two leadership types are shown in the chart below :
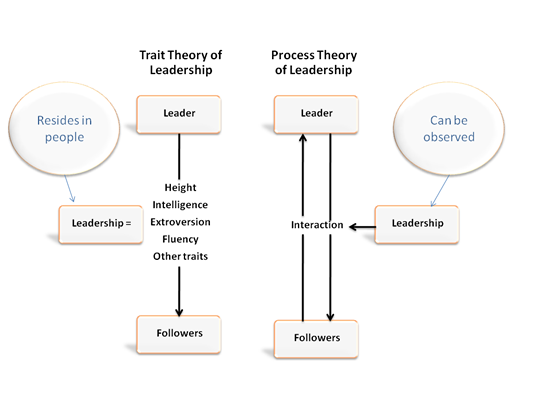
While leadership is learned, the skills and knowledge processed by the leader can be influenced by his or hers attributes or traits, such as beliefs, values, ethics, and character.
Knowledge and skills contribute directly to the process of leadership, while the other attributes give the leader certain characteristics that make him or her unique.
Skills, knowledge, and attributes make the Leader, which is one of the:
Four Factors of Leadership
There are four major factors in leadership :
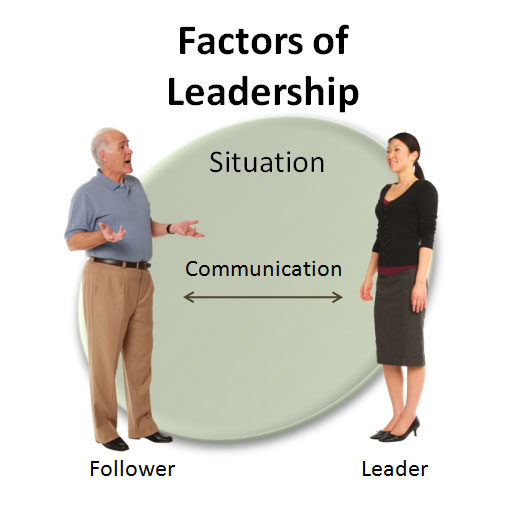
Leader
You must have an honest understanding of who you are, what you know, and what you can do. Also, note that it is the followers, not the leader or someone else who determines if the leader is successful.
If they do not trust or lack confidence in their leader, then they will be uninspired. To be successful you have to convince your followers, not yourself or your superiors, that you are worthy of being followed.
Followers
Different people require different styles of leadership. For example, a new hire requires more supervision than an experienced employee.
A person who lacks motivation requires a different approach than one with a high degree of motivation. You must know your people!
The fundamental starting point is having a good understanding of human nature, such as needs, emotions, and motivation. You must come to know your employees' be, know, anddo attributes.
Communication
You lead through two-way communication. Much of it is nonverbal. For instance, when you “set the example,” that communicates to your people that you would not ask them to perform anything that you would not be willing to do.
What and how you communicate either builds or harms the relationship between you and your employees.

Situation
All situations are different. What you do in one situation will not always work in another. You must use your judgment to decide the best course of action and the leadership style needed for each situation. For example, you may need to confront an employee for inappropriate behavior, but if the confrontation is too late or too early, too harsh or too weak, then the results may prove ineffective.
Also note that the situation normally has a greater effect on a leader's action than his or her traits. This is because while traits may have an impressive stability over a period of time, they have little consistency across situations .
Various forces will affect these four factors. Examples of forces are your relationship with your seniors, the skill of your followers, the informal leaders within your organization, and how your organization is organized.

Interest in leadership increased during the early part of the twentieth century. Early leadership theories focused on what qualities distinguished between leaders and followers, while subsequent theories looked at other variables such as situational factors and skill levels. While many different leadership theories have emerged, most can be classified as one of eight major types:
1. "Great Man" Theories:
Great man theories assume that the capacity for leadership is inherent – that great leaders are born, not made. These theories often portray great leaders as heroic, mythic and destined to rise to leadership when needed. The term "Great Man" was used because, at the time, leadership was thought of primarily as a male quality, especially in terms of military leadership. Learn more about the great man theory of leadership.

2. Trait Theories:
Similar in some ways to "Great Man" theories, trait theories assume that people inherit certain qualities and traits that make them better suited to leadership. Trait theories often identify particular personality or behavioral characteristics shared by leaders. If particular traits are key features of leadership, then how do we explain people who possess those qualities but are not leaders? This question is one of the difficulties in using trait theories to explain leadership.

3. Contingency Theories:
Contingency theories of leadership focus on particular variables related to the environment that might determine which particular style of leadership is best suited for the situation. According to this theory, no leadership style is best in all situations. Success depends upon a number of variables, including the leadership style, qualities of the followers and aspects of the situation.

4. Situational Theories:
Situational theories propose that leaders choose the best course of action based upon situational variables. Different styles of leadership may be more appropriate for certain types of decision-making.
5. Behavioral Theories:
Behavioral theories of leadership are based upon the belief that great leaders are made, not born. Rooted in behaviorism, this leadership theory focuses on the actions of leaders not on mental qualities or internal states. According to this theory, people can learn to become leaders through teaching and observation.

6. Participative Theories:
Participative leadership theories suggest that the ideal leadership style is one that takes the input of others into account. These leaders encourage participation and contributions from group members and help group members feel more relevant and committed to the decision-making process. In participative theories, however, the leader retains the right to allow the input of others.

7. Management Theories:
Management theories, also known as transactional theories, focus on the role of supervision, organization and group performance. These theories base leadership on a system of rewards and punishments. Managerial theories are often used in business; when employees are successful, they are rewarded; when they fail, they are reprimanded or punished. Learn more about theories of transactional leadership.

8. Relationship Theories:
Relationship theories, also known as transformational theories, focus upon the connections formed between leaders and followers. Transformational leaders motivate and inspire people by helping group members see the importance and higher good of the task. These leaders are focused on the performance of group members, but also want each person to fulfill his or her potential. Leaders with this style often have high ethical and moral standards.

Top 7 Steps To Develop Leadership Skills
If you want to set an example for others to follow, may we suggest the following check-list?
- Test the waters: find out what people think about your style of management. This could be a real eye opener, and the key to making changes to your leadership style. Employ a 360 degree approach wherein you receive feedback from your team members and peers. Let your team in on the objective behind the survey. A relaxed and open environment will help draw out their honest opinion.
- Listen hard: when your team members speak to you about all their work related worries, hear them out. You could convey empathy, suggest alternatives and create harmony within the team. GREAT LEADERS ARE GREAT LISTENERS!!!!!
- Connect: take complete responsibility for how you are heard. Always rephrase your message to make it sound positive. Effective communication is a fine art.
- Be a people’s person: an integral part of developing leadership skills is to learn to respect your team’s capabilities. Let the team members take decisions on certain issues. Trust them with their work; don’t be a watchdog.
- Lead by example: your team must believe in your integrity, and that you really mean what you say. Be prepared to put your money where your mouth is. It works like a charm!
- Share leadership: distribute tasks among group members depending on the situation and individual strengths. You become a better leader by involving more people in the leadership process.
- Evaluate your success in tandem with that of the team: your prime responsibility is to ensure success and development of the team. Focus on building their skills as this will enhance motivation and team performance. Remember, their success is yours too!

In each of the following choose from a scale of 1–5 which of these statements you most agree with or is most applicable to you.
Choose just one of the numbers 1–5 in each of the 26 statements.
Choose 5 for most agree/most applicable, down to 1 for least
agree/least applicable.
Copyright 2006 - 2023. ThinkPositiveLiveWell
All rights reserved.
ph: +96560443060
alt: +919689983542
jacksanf

